If you’re about to get an electric vehicle and are concerned about getting your EV charging situation sorted out at home without getting seriously charged—as in digging a big hole in your wallet—you’re reading the right post. I’ll explain how to fill your new vehicle’s “tank” and avoid those over-the-top electrical upgrade estimates.
I wrote this based on over a few years of experience on half a dozen Teslas of all available models, a Lucid Air, a Mustang Match-E, and a Polestar 2. That said, it’s safe to say what I’m about to mention applies to any EV. It’s collective wisdom from a group of friends and neighbors with different EV types.
To cut to the chase: Getting your car charged is generally more straightforward than you might think, and it’s much better than going to a gas station. If you live in a home with a garage (that has an electrical outlet) or an accessible outdoor socket, you’re already ready to leap. Think of your EV as another large appliance.
But there’s more to getting a car charged than plugging it in. Let’s start with the simple math of charging a vehicle.

EV charging: The general math of getting a car charged
Charging a battery is like filling a tank with water (or any type of liquid.)
The tank is the battery, and the water flow (pressure + pipe size) is the incoming electricity determined by Ampere (A) and Voltage (V). Combining the two, we have Wattage (W), which is, in this case, the tank’s volume or power flow.
Getting a bit nerdy: Voltage vs. Ampere vs. Wattage
Electricity is somewhat like water. There are three things involved:
- Voltage (V) or Potential Difference: The volume of electricity or the size of the potential force to be sent over the wire. It’s like the amount of water with its built-up pressure before you open the valve.
- Ampere (A) or Current: The size of the energy flow. It’s the pipe size in the flow of water. (Miliampere-hour or mAh is the unit for small batteries’ capacities)
- Watts (W) or Power: The amount of energy being delivered or consumed in real time. In water delivery, it’s the flow of the liquid from one container to another. Watts over a period of time—measured in Watt hour (Wh) or Kilowatt-hour (kWh)—indicate the amount of energy consumed, delivered, or accumulated and are used to show the capacity of large batteries, such as those in electric vehicles (EVs).
Here’s the relationship between these three:
V * A = W
The higher the wattage, the faster electricity can move from one place to another (charging speed) or the more energy it can produce (power output).
When the flow is constant, the rate of water entering the receiving tank is the same. So, how long it takes to fill a tank depends on its size.
After that, how long that full tank lasts depends on the usage or efficiency. Generally, the flow of electricity is always constant.
My Tesla Model Y Long Range’s battery has a capacity of 75 kWh. Per the EPA estimate—which is massively exaggerated—the car has a range of up to 324 miles on a full charge or 4.3 miles per kWh.
With that range, when plugged into a 120V (which caps at 15 A) socket, its charge rate is 5 miles per hour.
The actual real-world distance you can drive per kWh varies greatly depending on speed, load, wind, terrain, your belief in Elon Musk’s nonsense, and so on. But the rate at which electricity flows into the battery remains the same, which, in this case, is about 1.5 kW per hour (give or take).
This electric flow rate applies to all EVs that use the same battery technology. However, on heavier vehicles, such as the Model S or X, when plugged into the same 120V socket, this rate will translate into roughly 3 EPA miles per hour since the car requires more energy to move.
The point is this: The only way you can increase the charging rate is by using higher amps (and voltage). A larger battery doesn’t affect the charging speed; it only requires a long time to fill. That’s the case for all EVs.
Typically, you need a 240V socket if you want more than 15A. In the US, that means you need to make some serious electrical upgrades.
Or do you?
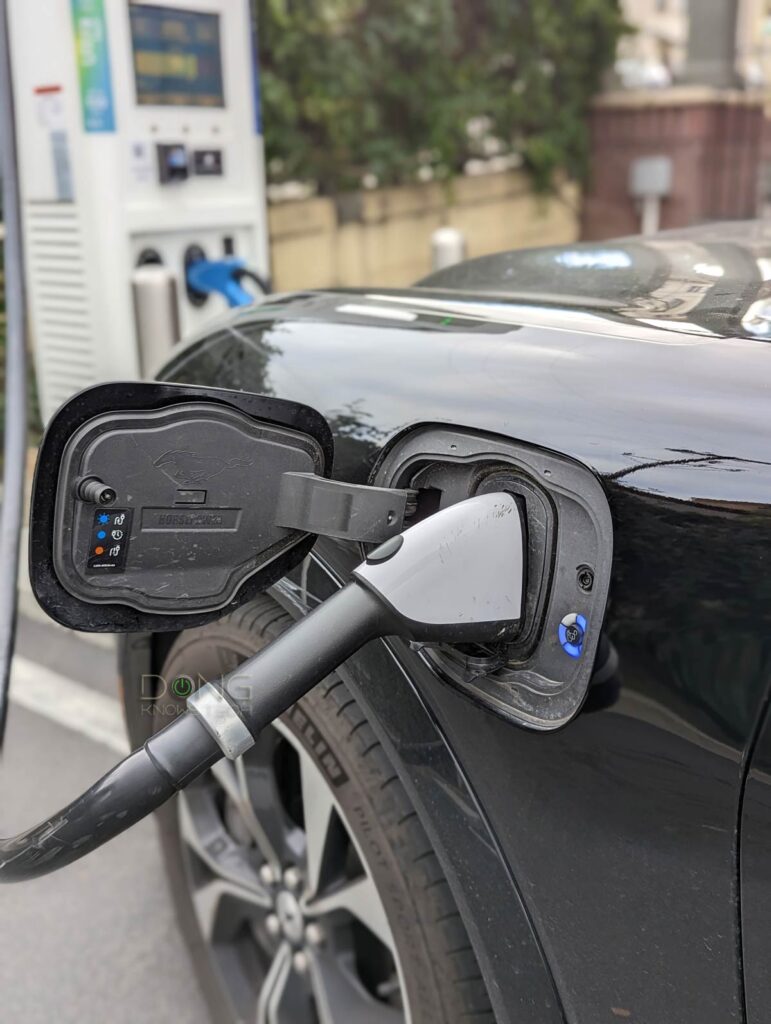

EV charging: It’s different from the pump
A few years ago, in preparation for the arrival of my first EV, a 2021 Model Y Long Range, I had difficulty figuring out our home’s electricity situation.
Chances are some of you are feeling the same right now when anticipating the delivery of your beloved vehicle or mulling over the idea of getting one.
Doing my search and listening to the advice of online EV “experts”—there are many of them these days—I got quotes from reputable electricians ranging between $5,000 to $15,000 in electrical wiring and breaker upgrades, depending on the scope of the work.
That’s not to mention the required permit and inevitable disruption—a home would have no electricity for at least a day during the retrofit.
It’s “all about the amps,” and it made sense. As mentioned above, the standard 120V socket in the US can push out a maximum real-world rate of 15 amps—often lower for safety reasons.
A Tesla Wall Charger needs a 60-amp breaker at 240V to deliver the fastest home charging speed, which gives a Model Y up to 42 miles (68 km) per hour of charging, or eight times the charging rate of the standard 110V socket.
And that’s all true—we need higher amps to deliver faster charging, which generally requires better wiring and breaker upgrades. The electricians didn’t lie. But in hindsight, I was looking at the whole thing from the mindset of a person who had always driven a car with an internal combustion engine (ICE). And so did the electricians.
The real question is this: How fast do you need to charge?

EV charging vs. filling the gas tank: You’ve got all night
With an ICE car, we “feel the pain at the pump,” as they often say during high gas prizes. And since we don’t (want to) spend much time there, it’s great that the tank only needs a few minutes to fill up.
And then what? You drive the car home, put it in the garage, and there it sits, doing nothing for hours.
With an EV, on the other hand, you can get the tank filled (slowly) whenever you’re home or basically when the car is not driven. So, in most cases, fast charging is unnecessary. You literally have got all night.
Slow charging is generally better for batteries. Unlike Superchargers that typically require conditioning the battery for optimum charging, you can plug/unplug the car arbitrarily with home charging with no additional effect on the battery or changing speed.
Take my Model Y, for example. If I plug it in the 120V socket when I get home at 5 PM, by 8 AM the next day, it’s obtained enough juice for some additional 60 real-world miles. And that’s enough for the day’s driving. And on the days I don’t drive, I can keep the car plugged in much longer.
Even if you drive a fair bit more than I do daily, the combined charging time of a regular socket over a week is generally fast enough.
So again, if you have a garage with a 120V socket or one that you can plug outdoors, you’re ready to get an EV as far as charging is concerned.
However, a faster charging option doesn’t hurt—among other things, it gives us more flexibility, such as charging during the off-peak hours when the cost of electricity is low.
But how fast is fast? Before we get there, let’s note one more thing about EV charging: the connector standards.


The two primary charging connector standards and three charging levels
In case it’s not obvious, to charge an EV, you need to connect it to a power source. The vehicle needs to have a charging port that fits the charger’s to-car connector—the part that goes into your EV’s charging port.
There used to be multiple standards, but in recent years, in the U.S., they have been reduced to two main ones:
- Tesla’s once-proprietary standard: Supports all levels of charging using alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). Originally made only for Tesla vehicles, this standard was opened for use to other car makers in November 2021 and received the name North American Charging Standard (NACS)—standardized as SAE Standard J3400. Since then, many EV makers have adopted it, and it’s estimated that by 2025, most manufacturers will use this standard for their cars.
- Combined Charging System (CCS): This standard supports the fastest charging speed (level 3) via DC but has built-in support for the AC-only J1772 standard slower charging speeds.
These two standards don’t physically fit, so converters are needed to use them interchangeably.
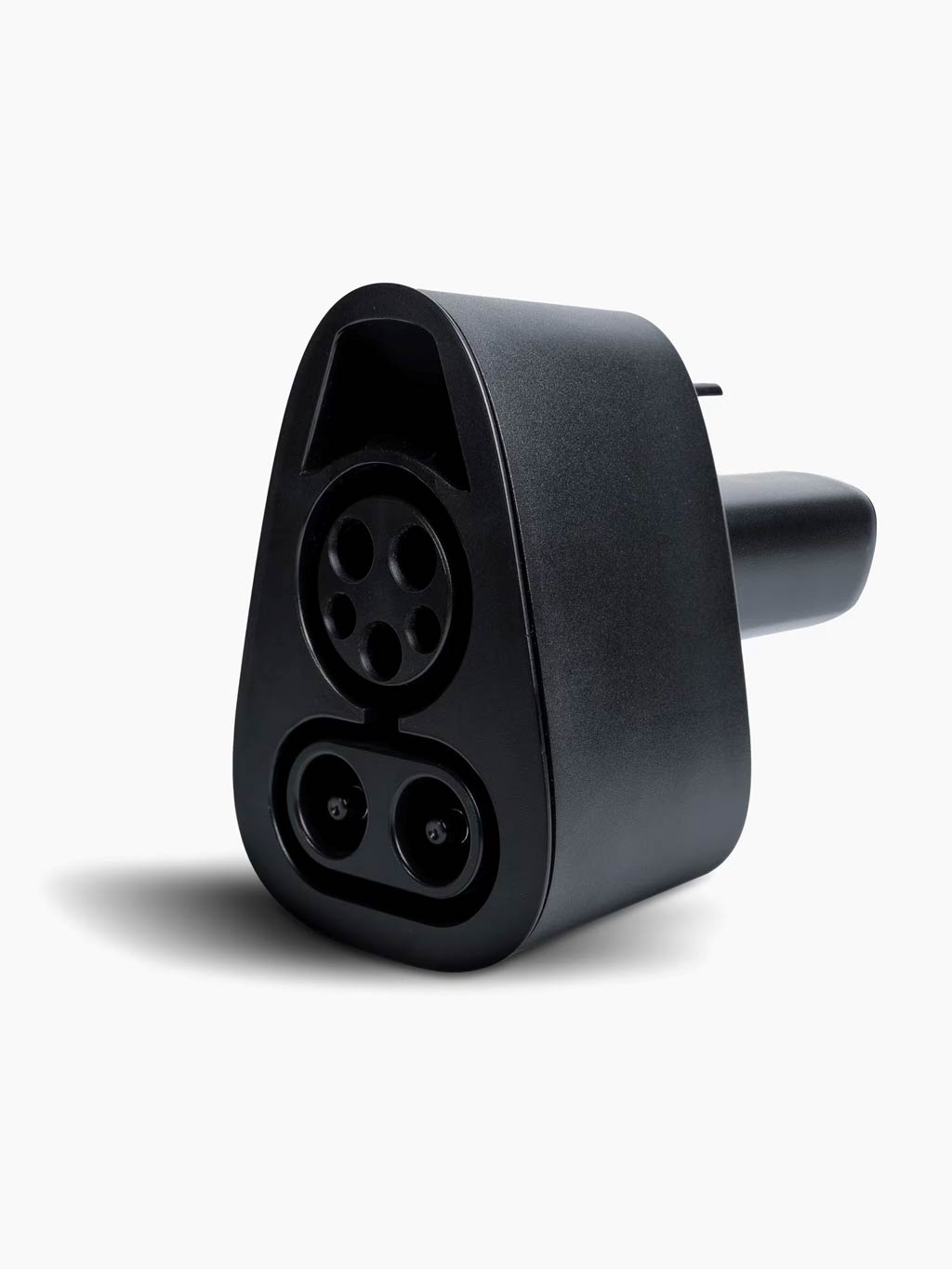


Since early 2023, Tesla has opened its Supercharging network to non-Tesla EVs (a NACS-to-CCS adapter is required for existing chargers). Increasingly, many non-Tesla DC chargers include a built-in Tesla connector. Eventually, NACS will likely be the winning standard.
CCS vs. J1772
A car with a CCS charging port supports both J1772 and CCS connectors.
Tesla owners take note: If you have the CCS adapter, you don’t need the J1772 adapter anymore.
For home charging, the Tesla-to-J1772 adapter, like the one below, has been available for a long time.

Now that we’re clear on how to plug a car in, below are three current charging levels.
Level 1 EV Charging: 120V (up to ≈ 15A)
- Electricity: Alternating current (AC).
- To-car connectors: J1772, NACS (Tesla).
- Charging rate: 3 to 5 Miles Per Hour (≈ 1.5 kW).
- Applicability: Home or anywhere with a 120V wall socket.

Level 1 charging is the lowest and, in the US, generally means you plug the car directly into a 120V outlet using the car’s default (often included) portable charger, technically called electric vehicle service equipment or EVSE.
There are also third-party portable chargers. While varying in design, costs, and possibly quality, all chargers will work with all EVs. It’s just a matter of getting the right adapter when necessary.
These “chargers” are essentially power cords. The charging function is inside the EV.
Apart from the 120V socket, most level-1 chargers also work with 240V sockets to deliver faster Level-2 charging speed.
Until April 17, 2022, Tesla included the Mobile Connector with its cars. It’s the company’s default Level-1 Charger.
Level 2 EV Charging: Up to 240 V (up to ≈ 80A)
- Electricity: Alternating current (AC).
- To-car connectors: J1772, NACS (Tesla).
- Charging rate: Up to 80 Miles per Hour (≈ 20 kW).
- Applicability: Home or anywhere with a 240V wall socket or a charging station.
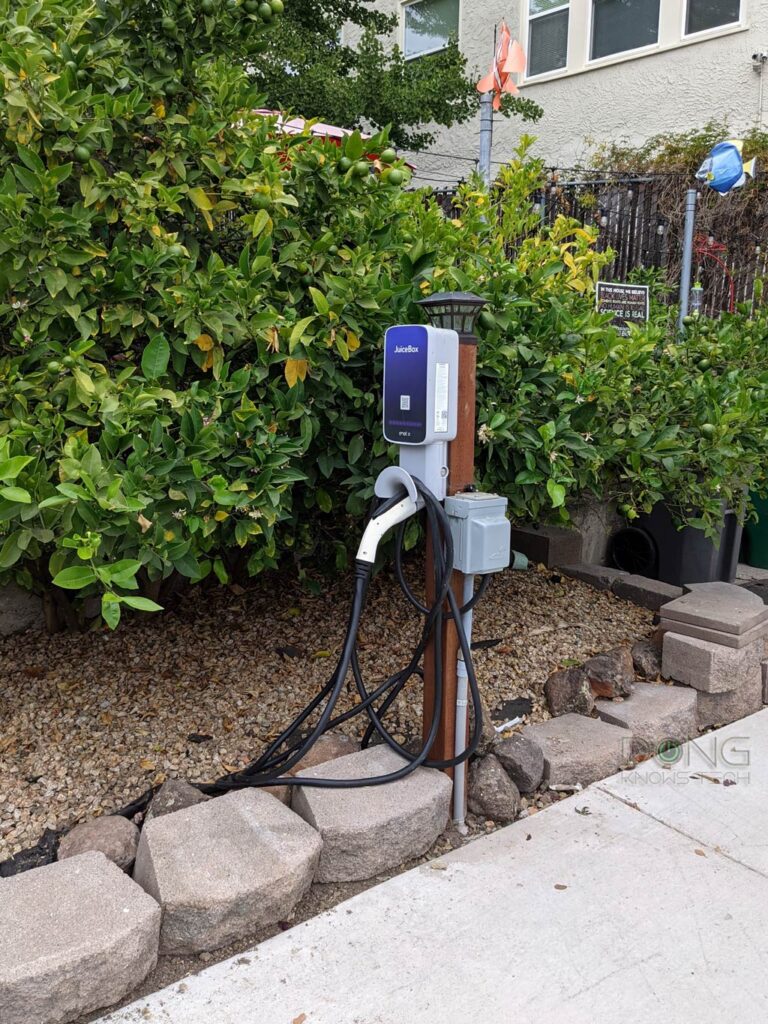

Level-2 charging is the fastest option you can install at home. It requires new wiring.
At the minimum, in the US, you’ll need a separate breaker for a 240V outlet, similar to an oven or dryer. Most EVs’ portable chargers work with 240V and 120V outlets via interchangeable to-wall adapters.
A charging station, such as the Tesla Wall Charger, requires new wiring. This type of charger must be wired directly into a 240V breaker and won’t work with any socket.
Level 2 can deliver between 15A to 80A of electrical flow and give an EV up to 80 miles in an hour of charging though 60 miles/hour is common.
Level 3 EV Charging: At least 400 V
- Electricity: Direct current (DC).
- To-car connectors: Combined Charging System (CCS) and NACS (Tesla).
- Charging rate: at least 3 miles per minute, up to over a thousand miles per hour.
- Applicability: Public charging station.

Level 3 charging equals “gas stations” for EVs—it’s the fastest charging option.
For years, Tesla’s Superchargers have been the most well-known Level-3 charging, with each charger capable of filling a Tesla’s battery from 20% to 80% in 20 minutes, or as fast as 5 minutes, depending on its wattage, which ranges from 75 kW to 250 kW (and even higher.) The higher, the quicker the charging rate.
In the US, most, if not all, non-Tesla Level-3 charging stations use the CCS connector, which encompasses the J1772 connector.
Many non-Tesla DC chargers include a Tesla connector.
Level 3 charging uses direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC), like in the case of Levels 1 and 2. Each charger costs tens of thousands of dollars. That’s not to mention the electricity cost.
Other than CCS, some Japanese cars also use a new connection called CHAdeMO for Level-3 charging. In the US, a CHAdeMO DC charger often includes a CCS and a Tesla connector.
Home charging: Only level 1 or level 2
For home charging, the portable charger (included with most EVs) is generally enough.
The portable charger of a Tesla is the Mobile Connector. Initially, it’s included with a new car for free, but starting April 17, 2022, it’s been an accessory you must pay extra for.
In any case, this charger is simply a glorified power adapter—the charging function is inside the vehicle. The point is that you can always buy a third-party portable charger that fits your usage and budget. They all function as power cords.
I’ll use my Model Y’s Mobile Connector as an example, but other portable chargers share a similar concept.
Though much bigger, the Mobile Connector is similar to a laptop’s power adapter—it can handle power input from 110V to 240V and various amps outputs via different to-wall adapters that fit different wall sockets.
By default, the charger includes the region’s standard adapter head. In the US, that adapter head is the NEMA 5-15, the three-prong plug for any wall socket around your home. In this case, you can plug it right in, just like a phone, and it will charge the car a few miles per hour, as mentioned above.

Using different adapter heads out of the bundle in the above picture, you can charge the car at faster rates, depending on the power output of the fitting socket.
In the US, the best option is the NEMA14-50—a popular plug for electric ovens or dryers. With it, the Mobile Connector works with a 240V outlet to draw up to 32 amps of power to deliver a filling rate of around 7kWh. (For my Model Y, that’s about 30 miles per hour.)
Starting in August 2022, in the US, the Mobile Connector includes the Nema 5-15 and NEMA 14-50 adapters.
The actual amps the car’s charger draws depend on the real-time condition when you plug it in, and for Level-2 and Level-1 charging, users generally have control over that. With a Tesla, you can use the mobile app to make the car draw lower amps than available.
So, a 240V Level-2 charging option will also allow you to trickle charge the car when you’re not in a hurry.
A typical home charging station
In my case, I decided not to do any major breaker upgrade or install the Level-2 Tesla Wall Charger.
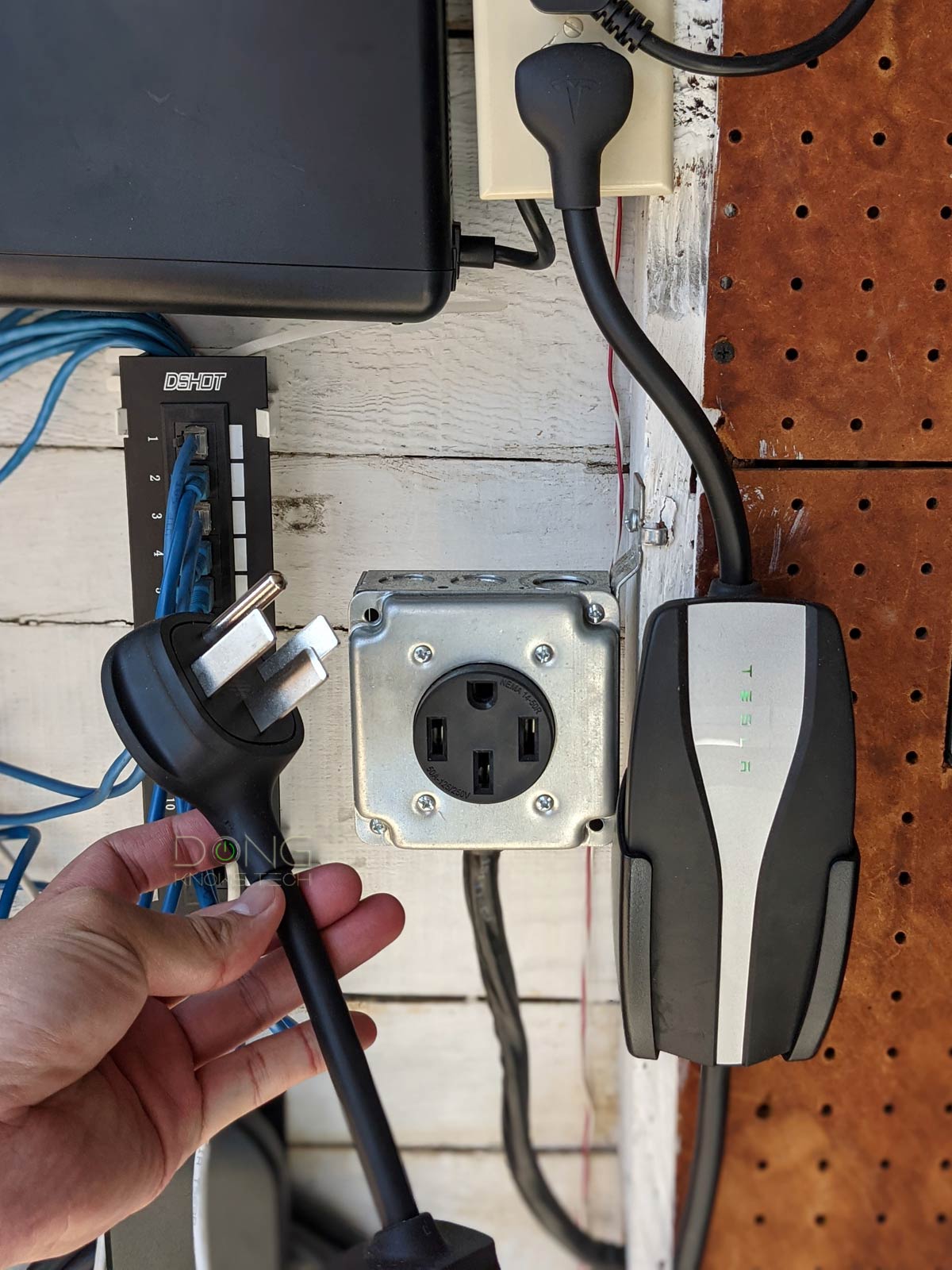

Instead, I had a licensed electrician friend install a 240V 40-amp outlet by upgrading an existing line and using the NEMA 14-50 adapter head for my Mobile Connector. All that cost less than $500. It’s important to get this done correctly. I’d recommend using a professional for the job. Also, generally leave the NEMA 14-50 adapter in the socket—it’s best not to remove it often.
With the new socket, the Mobile Connector can deliver up to 32 amps and fill my Model Y at around 30 miles per hour, or about half the speed of a real level-2 charging station. Still, that’s fast enough for a full overnight charge.
I later got a second Mobile Connector, mounted it permanently in the garage as my home charging station, and kept the original with the car.
But that’s proven to be already more than enough. Most of the time, I use the Tesla app to tune that down to 20 amps or lower to slow down the charging rate—there’s no need to put an unnecessary strain on the wiring.
I find it a fun challenge to make the car have an exactly specific amount of energy before leaving for a trip.
Once in a while, I still plug my car into a 120V socket, especially when traveling, as I’d need to charge from a rental house or a campsite, and that has always been sufficient in most cases.
My routine has been to plug the car in and let it do its thing when I get home. I generally set the max charge at 180 miles, about 55% of the battery’s capacity, which is more than my typical day’s worth of real-world driving.

EV charging: Battery types and best practices
Generally, batteries are at their best when they are not completely empty or full.
In practice, with EVs, that depends on the battery. All EVs use Lithium-ion batteries available in two types differentiated by mainly the materials used for their cathodes.
The first type is nickel-cobalt aluminum (NCA), a.k.a nickel manganese cobalt (NMC), which is expensive but light and can be charged relatively fast.
Generally, NCA batteries have limited charging cycles and should typically be charged at 80% to maintain longevity. It’s the type currently used in most existing EVs.
In 2022, a new sub-set of Lithium-ion batteries, lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP), went into production. This type is heavier and takes longer to fast-charge. So, it’s not ideal for long-range or performance applications.
In return, LFP is less expensive—it doesn’t require rare materials like NCA. Most importantly, it has significantly higher charging cycles to last much longer and can be charged regularly to full without degradation, offsetting the shorter range and easing overcharging anxiety compared to NCA.
| Nickel-Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) | Lithium Iron-Phosphate (LFP) | |
| Used in (by early 2023) | Most existing EVs Some high-end future EVs | Tesla Model 3 (2022 and newer) Tesla Model Y SR (2022 and newer) Most future EVs |
| Weight | Heavy | Heavier |
| Range | Longer | Long |
| Level-3 Charging Speed | Faster | Fast |
| Home Charging Speed | Slow | |
| Recommended Charge Level | 80% | 100% (fully charged once a week) |
| Charging Cycles (longevity) | up to 3,000 cycles | Up to 10,000 cycles |
| Thermal Runaway | 410° F | 518° F |
| Risk of Fire | Very Low | Extremely Low |
| Price | Expensive | Less expensive |
The two types of batteries are the same in principle and are differentiated only by the materials used for their cathodes.
So far, only Tesla has used LFP batteries in its fleet, but other car makers will follow suit. LFP batteries are also under further development and optimization to deliver better performance. It might eventually replace NCA in the future.

Generally, in daily usage, it’s best to use an EV with a battery between 20% and 80% because of the following reasons:
- You can charge it the fastest. It takes much shorter to fill a battery from 20% to 80% than from 80% to 100% (*).
- It outputs energy the most efficiently.
- The (NCA) battery itself can last the longest without degrading.
(*) Charging a battery is like parking cars in a large parking lot, where each car is an electron. When the lot is empty or half-full, it’s much faster to park a car. As the stalls get filled up, finding a spot for an incoming car becomes much harder and takes a longer time. The same thing can be said about the opposite: a battery can discharge more efficiently when it’s not full.
This idea of giving stuff some “breathing room” exists in ICE cars, too. Most gas stations suggest that you don’t “top off” the tank, and all mechanics will tell you that letting the car run completely out of gas is a bad idea. Running the car till the gas tank is empty means you will let harmful sediments into the engine.
Generally, right before you go on an extended trip, it’s fine to charge any EV to 100%. When you’re on the road, plan to get it plugged in before the battery gets lower than 10%. On a long drive with multiple legs, it’s best to charge the car enough for the next DC charger (with some to spare).
No matter which type of battery, don’t drive your EV until it’s completely out of juice. Unlike ICE cars, EVs need electricity to keep their subsystem running.
Finally, monitoring your car’s battery using percentages rather than miles is recommended. The range estimate is so greatly inaccurate and widely exaggerated, especially in Tesla’s case, that it’s dangerous to count on. But if you use it, discount at least 30% to be safe—more in this post about my Model Y’s real-world range.
Tesla Supercharger
It’s impossible to talk about EV charging without mentioning Tesla’s Level-3 Supercharger network, the most comprehensive charging network worldwide which likely will become the standard for EV charging when/if all car makers adop the NACS charing port.
In fact, the only reason many Tesla drivers get a Tesla is because of the company’s Superchargers. They make long road trips possible. There are two things worth noting about Tesla’s supercharging network.
First, it’s ubiquitous and super convenient to use, specifically:
- When the car’s battery is low, its screen will show nearby Supercharging stations on the map, which is much more convenient than Google Maps, which has EV chargers as points of interest.
- Punch in a destination on your car, and the car’s navigation will include stops charging station(s) if need be.
- When you pick a charging station, the car automatically optimizes its battery for fast charging by getting it to an ideal temperature.
- Drive the car to a charging station, plug the charging cord into the car, and you’re all set.
You can manage the charging level (and payment) via the car’s touchscreen or the app. But if you don’t do anything, the vehicle will be charged at your predetermined level, or enough to get to the next charging station of the trip, based on the car’s current rate of consumption and real-time road and weather conditions.
Secondly, a Supercharger station can charge a car fast. Starting at 70 kW and going as high as 250 kW, a station can fill a Model Y’s battery from 20% to 80% in 30 minutes or under 10 minutes, respectively.
Tesla also has Level-2 Destination Chargers, which are similar to home chargers and top out at around 60 miles per hour.
Supercharger and cost
The actual price varies from area to area and even time of day, but generally, on a bad day in my high-energy-cost state of California, the price to fill my Model Y from 20% to 80% is about $25—that’s easily over 100 real-world miles worth of energy.
On average, on a long road trip, I paid around $20 each time I used a Supercharger. Note that the company charges idle fees—you need to remove your car when the charging is done.
So, depending on where you are, the cost for a full charge via Supercharger varies from $30 to $60—the cost is similar if you use a non-Testa charging station. Still, if you have to rely on level-3 public charging, your situation is not ideal for driving an EV, both in terms of convenience and energy cost. Get your home charging situation sorted out first.
EV charging: The takeaway
There you go. If you have a wall socket and maybe a long extension cord, chances are your home is ready for an EV. There’s no need to get fancy with electricity.
Here are a couple of recap bullet points:
- You don’t need to charge an EV at a fast rate at all times and every single time. You’ve got all night.
- In most cases, any existing 120V socket (level-1 charging) is enough to switch to EV. Especially for daily commuting or local driving.
- Unless you drive more than 100 miles daily, level-2 home charging (a charging station or the combo of a 240V socket + a mobile charger) is more about convenience and flexibility than necessity.
- You can always take the car to a public Level-3 charging facility when needed, the way you get an ICE car’s tank refilled. (But if public charging is your only option, EVs generally don’t quite make sense—get your home charging sorted out first.)
Here’s the bottom line: Getting an EV charged is much more readily available than filling an ICE car with gasoline. All you need is a wall socket (a long extension cord may come in handy) or a couple of solar panels.
An interesting fact: gas stations need electricity, too. And they all have a socket somewhere for you to plug in your EV if you know how to ask nicely and have a long extension cord. But when out of gas or during a power outage, there’s not much the station can do about your ICE vehicle’s empty tank.
Dong’s note: I first published this piece on February 8, 2023, and updated it on April 2, 2024, to add relevant, up-to-date information.



Hi Dong,
Great post! I just got a Model Y Long Range and love it. Few follow up questions to your post:
1) If my Model Y Long Range was manufactured December 2023, does that mean I have the LFP battery? Or how can I tell?
2) My friend’s referral got me six months of free supercharging, so I’ve only ever been using superchargers (since it’s free) to charge to 80%. I live in an apartment complex that offers Level 1 and Level 2 charging at a cost. Should I start to use those instead of going to superchargers to “fill” the car? I’m interested in increasing the longevity of the battery.
3) When you say, “It’s important to note, though, that if you have to rely on level-3 public charging, your situation is not ideal for driving an EV — get your home charging situation sorted out first.”… are you saying this because of the inconvenience of finding and using superchargers (as a primary source to recharge) or because they will cause faster battery degradation?
Thanks!
Hi Arian,
1. If your recommended charging level is not 100% then your battery is not LFP. Chances are it’s not considering your trim.
2. I wouldn’t worry about it. The difference is negligent, just don’t charge over 80% or drain below 20% frequently and you’re good. This is the most important by far.
3. The convenience and most importantly the cost. Supercharging can be quite expensive, easily two or three times the cost of home charging, even more.
I’d recommend taking a few road trips during the time you get free charging. Super fun. Don’t forget to get a tire repair kit as I mentioned in the related post.
Thank you for the reply and recommendation!
I just ordered the tire repair kit 👍🏼
Our first drive with the car was a trip from Bay Area to Orange County a day after we took delivery. Probably not the best time to learn a new car, especially in the rain and fog, but it was still a fun and a good learning experience and we plan to take more trips to and from.
I’ll continue to charge to 80% at superchargers since it’s free for me and two are close to me. Thanks again!
By chance, a friend of mine and I left for Los Angeles from San Francisco on the same day at the same time. Him in his Model 3 Performance and me in my BMW 330i. It is a 500 mile drive one way with average 80mph highway speeds. We both stopped for lunch in the middle of the drive. He arrived 2 hours after me. He had to supercharge his car twice – once at lunch and once at a popular station with a 15 min wait line. I did not have to refuel and arrived with 1/5 a tank of gas left. In comparison, I did the same drive with another friend in his hydrogen EV. We stopped once for refueling (< 1 min to refuel and tons of hydrogen stations in California) and arrived in the same amount of time as a gas powered car. Much more convenient and consumer friendly than a battery EV!
Living in a condo meant home charging is a no go. Last month when purchasing a new car – I got another gas powered vehicle. I'll wait for solid state batteries and faster charging (instant charging?) before making a move.
That’s about right, and your assessment is correct, Philip. I’m from the Bay Area and have often taken that same route to Disney Land. The Model X and S have a bit more range, but gasoline is still superior to battery in energy density. Still, for a long drive, generally, it’s a good idea to take a good break after three hours of driving anyway — for EVs, you can also take more frequent shorter breaks. I wrote more about that in this post about EV’s real-world range.
I agree with Luz. This is one of the best introductions to EV’s I have seen. And I still think the best antidote to range anxiety is great big signs near every cluster of charging stations. Ann Arbor, for example, has about 40 distributed among four public parking garages. And zero signage.
Thanks for the kind words, Mike. And yes, there are more and more charging stations now. You can have them displayed on Google Maps — search for “EV chargers.”
Thanks for the timely information. I am curious if an EV is the right answer for me as I have a 130 mile commute when I go to the office. I may eventually be able to charge at the office, but I can plug in using the included charger.Tesla does have several charging stations near me and along the route.
For that much driving, you will need a 240V outlet for Level-2 charging at home, Huley — you’ll get a full charge overnight.
For your case, it’s best to get the Model 3 or Model Y Standard Range (2022 or newer). Either comes with a new LFP battery that you can charge to 100% daily without worrying about degradation. A full charge will give you 270 EPA miles (or more if you get the expensive trim), enough for your drive to work and some. Then, if you can plug in at work, you’ll add 40 miles (via a normal 110V socket) or another full charge if you have a level-2 charger. Or you’ll need to use a supercharger once on the way back.
Note that how far you can drive on a full charge depends greatly on how you drive it. More here. I guess you’ll use up over 200 miles for that distance initially — it’s very hard to resist.
The Model 3 is the most fun Tesla for a commute. More fun than the Model Y or even Model X — some even like it more than the Model S. I speak from experience. 🙂
In short, with some planning and getting used to, it’ll work, and chances are it will work out much better than you think. I’d say go for it.
Thanks for that additional information.
I need to correct he commute distance. It is about 130 miles total (65 each way). 200 miles is about how far I drive in a day considering the other things I need to do.
I will go to my local Tesla dealer and test drive one.
Thanks for the valuable information, especially on the speeds and range calculations.
Sure, Huley. Have fun! I’m excited for you. It will get a bit tight, but the 120V socket is probably enough for 150 miles/day of driving as long as you plug the car in and charge it whenever you’re home and topping the car off during the weekend.
I will be test driving the Model 3 this afternoon. I am looking forward to seeing what it can do. It potentially can save me a lot of money.
How much do you pay at one of the Tesla superchargers?
I mentioned that in this post, Huley, but that generally varies from one area to another. In CA, which has very high energy costs, I typically pay about $18 each time I use the charger. On our last trip from the Bay Area to Cambia (CA), about 230 miles away, on my Model Y LR, loaded with a family of five and camping gear, I paid about $40 in charging round trip — I managed to get plugged in (120V) overnight at the cabin for free, though. We did drive around the area during our stay but only got charged at Superchargers on the way there and back. I drive quite conservatively, though.
Thanks for that reply. I went back through the post and picked up some more information which will help me.
I saw and experienced the Model 3 today! It was much better than I believed it to be and even better than you hinted. This is a great car! I want my wife to experience my joy first hand as we will be testing it again. We are also going to shop around for a few more EVs then decide on one. These are the future, as you said in your post. I did really enjoy my test drive with it. The salesperson turned me loose after watching a video showing me how to use and set up the car. It was the Performance Edition that I drove, which was the first time I drove an EV. If more people tested them, they would get a sense of just how good they are. For the purpose I plan to use it for, it should work well for me. The salesman even hinted that I could go with a Rear Wheel drive model as well. If I have any questions, I know where I can get unbiased answers to them! Thank you so much for posting about your experience! I will be reviewing the posts and extracting information from them!
Glad you enjoy the test drive, Huley. For your needs, though, I’d recommend against the performance model or larger (fancier) rim. They are just money down the drain since you’ll get a shorter range and more expensive cost (for tire) down the road with nothing but the look in return. (More about Tesla’s tires and rim in this post.)
If you go with the Model 3, go with the rear wheel drive with the standard wheel, you’ll note almost no difference in performance and a less bumpy ride, plus better range. (I just got one for my wife, as you can see in the security vid of this review.)
If you want with performance (or Plaid), that only makes sense in Model S or Model X. Still, it’s a waste of money. (I have friends who have those.)
I’m no fan of Elon Musk (as you will note), but for your long commute need, chances are the Model 3 fits the bill the best, and the Model Y will work great, too. But if you can get the charging sorted out, any EV is better than a gas car.
By the way, buying a car from Tesla is very different from any dealership. There’s no haggling, and the reps all have a kind of “take it or leave it” attitude. But I’d take that over any car salesman in a heartbeat.
Good luck!
Thank you for the sound advice.
It is much appreciated!
would you marry someone who needs this much maintenance and planning. Has anybody ever heard of the KISS principle. Keep It Simple Stupid. Hope you never have an emergency and have to charge your car first.
What maintenance and planning, george? If your ICE car is out of gas during an emergency, you’ll also have to go to the gas station. The difference is with an EV, chances are its battery is *never* empty when at home — in most cases, keeping the battery from getting over 80% charged is more of an issue though it’s as easy as picking the appropriate setting. Did you even read the entire post?
Oh come on. Why would your ICE vehicle be empty in an emergency when it’s so simple to ensure that is never the case? It’s good practice not to let a petrol or diesel tank go down to almost empty anyway. And surely many EVs will *frequently* be empty soon after a day’s driving and still be fairly empty until half way through the night?
Because it’s an emergency, Ross, which, by definition, is not something you can anticipate or plan. Get a good EV, and you’ll know how wrong your statement is. I used many ICE cars before, and I switched to EVs not because I couldn’t afford another. Take my word for it.
Great post! The only problem is that people who are fearful of EV’s are unlikely to read your column or other tech-oriented columns.
d
I own a modest 2020 Chevy Bolt and would never go back to a gas-guzzler. Perhaps more to the point for the timid souls, I am in my 80’s. And I thinkit is a good idea is to refer skeptics to a standard search engine or one of the several cell phone apps that provide charger location information.
Thanks, Michael. Google Maps have EV chargers as points of interest — just like gas stations or grocery stores, etc. And all charging apps have a map of their own.
Great post, Dong! Thanks for sharing your expereince. The idea that an EV is basically an appliance is on point. Electric cars are the future, no doubt.
👍