Kudos to you for reading this right now. You’re clearly online! Often, folks worry about broadband Internet troubleshooting when they can not connect, which is a terrible time to start googling for solutions. Such is life.
The point is that it’s good to be well-prepared. Give yourself a pat on the back! Done? Let’s dive in!
Important note: Wi-Fi and the Internet are two different things—you’re reading about the latter. This post on Wi-Fi dropping and local connection issues will help tackle the former.

Broadband Internet Troubleshooting: The A-B-C simple steps
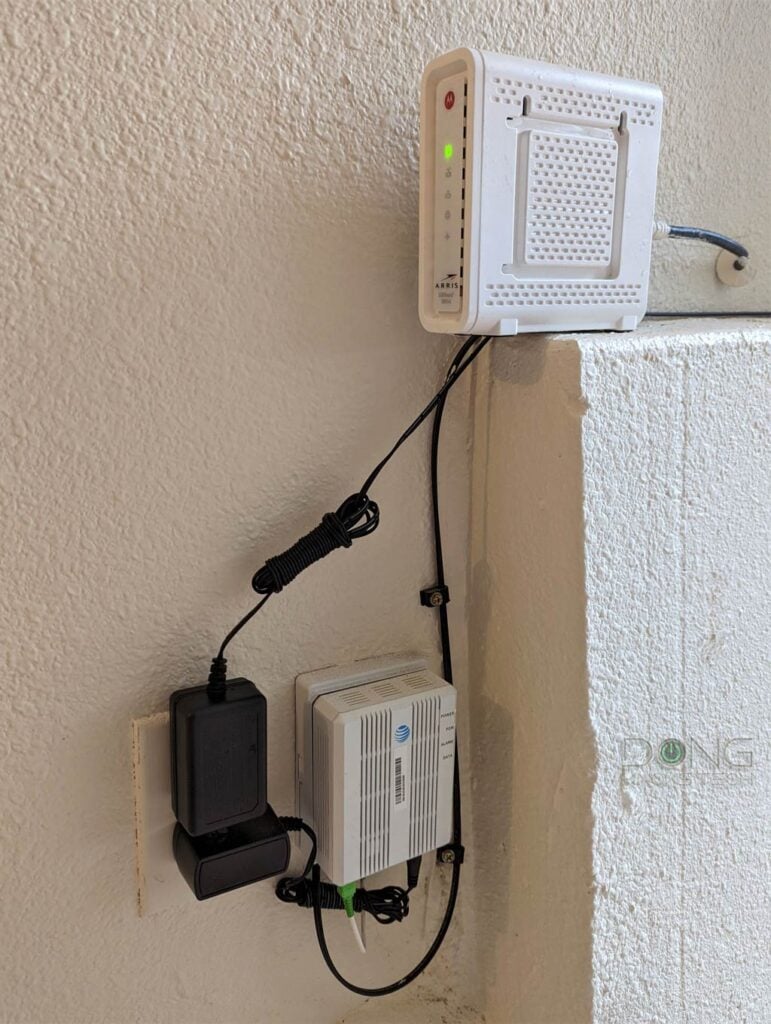
Every network is different, but all have a broadband terminal device—likely a cable modem or a fiber-optic ONT—and a router. Sometimes, those two are combined in a single hardware box called a residential gateway.
Whether you have an ONT, a modem, or a gateway, you can apply these A-B-C steps when you can’t get online. Let’s start with A: the basics.
A. Take care of the basics
These are the basic things you should do first, in the order below or in whichever way that’s convenient. You can also do just one or all of them until the issue is fixed.
1. Restart the hardware
Often, a simple restart will fix the connection issue. Specifically, locate your Internet box or boxes, unplug them from the power, wait for a few seconds, and then plug them back in and make sure they are turned on. Now, wait for a few minutes for things to reboot.
And that might just be it.
2. Is the service (or website) available?
If you conclude that you’re disconnected because you can’t access a particular website (like dongknowstech.com) or service (such as Netflix), the first thing to do is try a few different sites or services to see if you can reach them. If you can, the issue might have nothing to do with your Internet access.
When a specific party or website on the Internet is unavailable, all you can do is wait it out.
3. Is your Wi-Fi turned off?
That’s right! You might have accidentally turned off the Wi-Fi on the router or the device you’re using.
This issue is common in laptops where you might inadvertently switch on the Airplane mode. It also applies to some media streamers and IoT devices, such as network printers or IP cameras, that have a button that toggles the Wi-Fi on or off. Some routers also have a similar on/off switch for the Wi-Fi function.
Well, turn the Wi-Fi back on!
4. Which Wi-Fi network are you using?
You need to be aware of which Wi-Fi network your device is connected to. For example, you cannot fix anything if your device connects to your neighbor’s Wi-Fi instead of yours.
Connecting to the wrong Wi-Fi network will cause local tasks—such as network printing or file sharing—to fail. Most importantly, when disconnected, you’d be beating on the wrong bush.
5. Are the cables intact and plugged in securely?
This issue can be relatively rare, but it doesn’t hurt to ensure all the cables and wires are plugged in correctly and intact—not cut, broken, or chewed up by pets.
All hardware devices (router, modem, ONT, gateway, switches, etc.) must be plugged into power and turned on. They also need to be connected in the correct order using the correct ports.
B. Figure out where the issue is
If you have taken care of the housekeeping above and the issue persists, it’s time to do some digging to locate the problem.
Two things to keep in mind:
- Can you connect a device to your Wi-Fi network? If not, or the Wi-Fi network is unavailable, such as you don’t see the SSID on your phone, the problem is likely at the Wi-Fi router.
- If you can connect to your Wi-Fi network but cannot access the Internet, the issue is likely at the broadband terminal device.
Let’s look at the specifics.
C. Broadband Internet troubleshooting: Checking the hardware
Again, your terminal device is the hardware piece that connects your home to the Internet.
In a standard setup, the terminal device is often the cable modem or fiber-optic ONT. In this case, it’s the device your router connects to. If you use a gateway, keep in mind that the terminal device is part of the single box.
A quick refresher: What is your Internet setup? The table below gives you some quick hints on the broadband hardware.
| Broadband Terminal Device | Wi-Fi Router | Gateway | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | |
| Composition | A broadband receiver device that connects to the Internet, often a cable modem or a fiber-optic ONT | A router with a built-in Wi-Fi access point, including the primary unit of a Wi-Fi mesh system. (a 2-in-1 device) | A single device that includes a terminal device and a Wi-Fi router in one box (a 3-in-1 device) |
| Internet-Related Role | Brings the Internet to a single device (the router) in your home via the service line | Brings the Internet from the terminal device to local devices for them to communicate with the outside world via network cables or Wi-Fi signals. | Both |
| Local Network Role | None | Creates a local area network (LAN) for devices to communicate internally within the home network. | Both |
| IP Address Handling | Maintain a wide area network (WAN) public IP address | Assigns and manages LAN private IP addresses to local devices | Both |
| Notes | 1. Easy to replace or upgrade. 2. Can connect a single wired device, the router, to the Internet. | 1. Easy to replace/upgrade. 2. Need a terminal device to connect to the Internet, but works with all Internet types. 3. Share the Internet connection (of the terminal device) to multiple devices in the network via Wi-Fi or network ports. 4. Will create a double NAT when connected to a gateway. 5. Most models can be configured to work simply as an access point | 1. Support only the broadband type of the service port (cable or fiber-optic), but can immediately share Internet access with multiple local devices. 2. Impossible to replace or upgrade just the terminal or router part, which is often limited in features and hardware capability. 3. Some models can be “bridged” to work as simply a terminal device. |
Tip
If you have a separate modem/ONT and a router, the network cable connecting the two must go into the router’s WAN port, and it should be securely plugged in at both ends.
1. How to handle a Cable modem or a Fiber-optic ONT
The tabs below contain detailed steps to check the Internet signal on a Cable modem or a Fiber-optic ONT.
All modems have a broadband status light, a.k.a “signal” or “sync” light.
In most modems, this light tends to have a shape or a label that suggests it is related to the Internet. Often, it resembles a little globe or has the letter E.
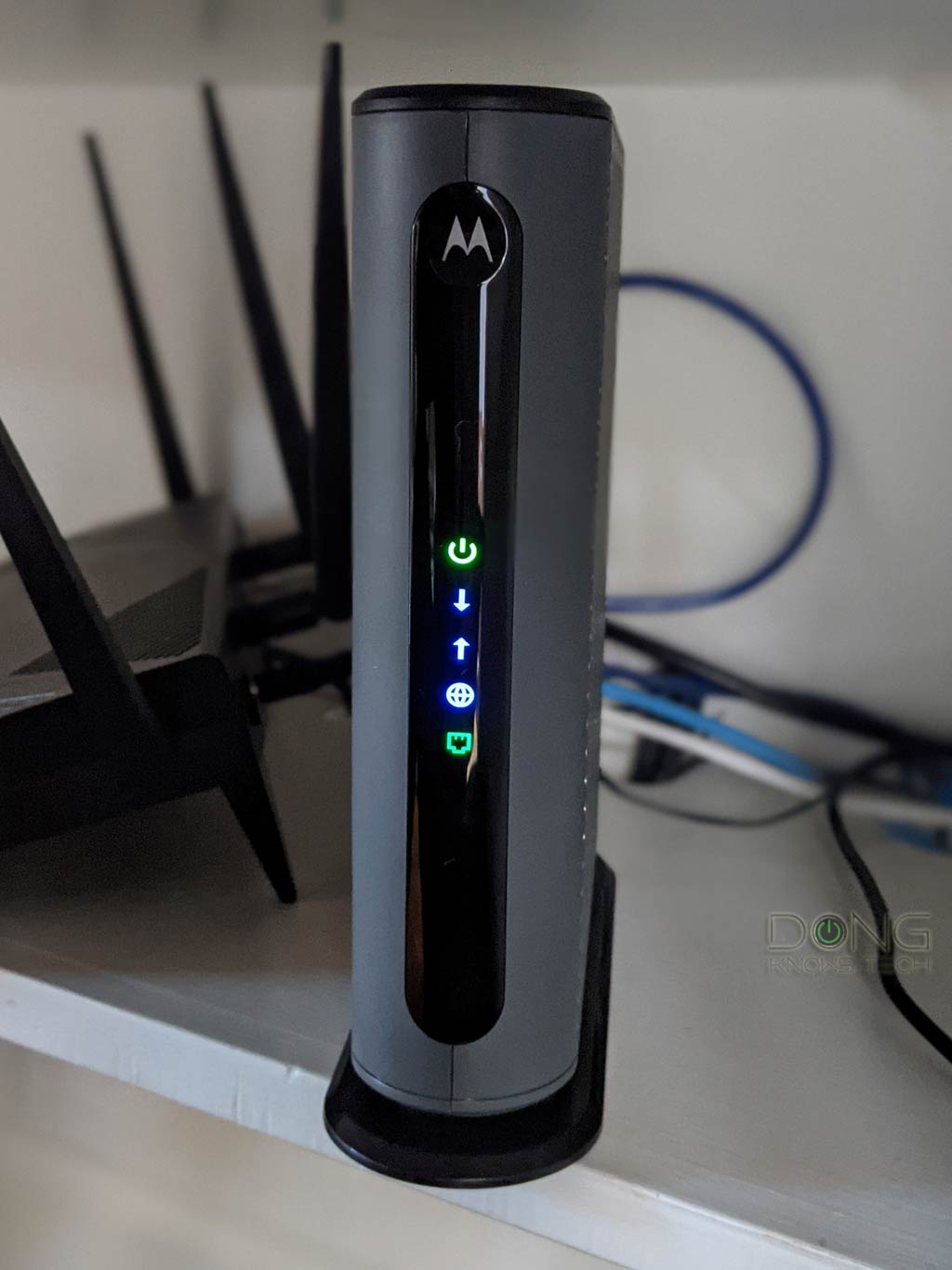
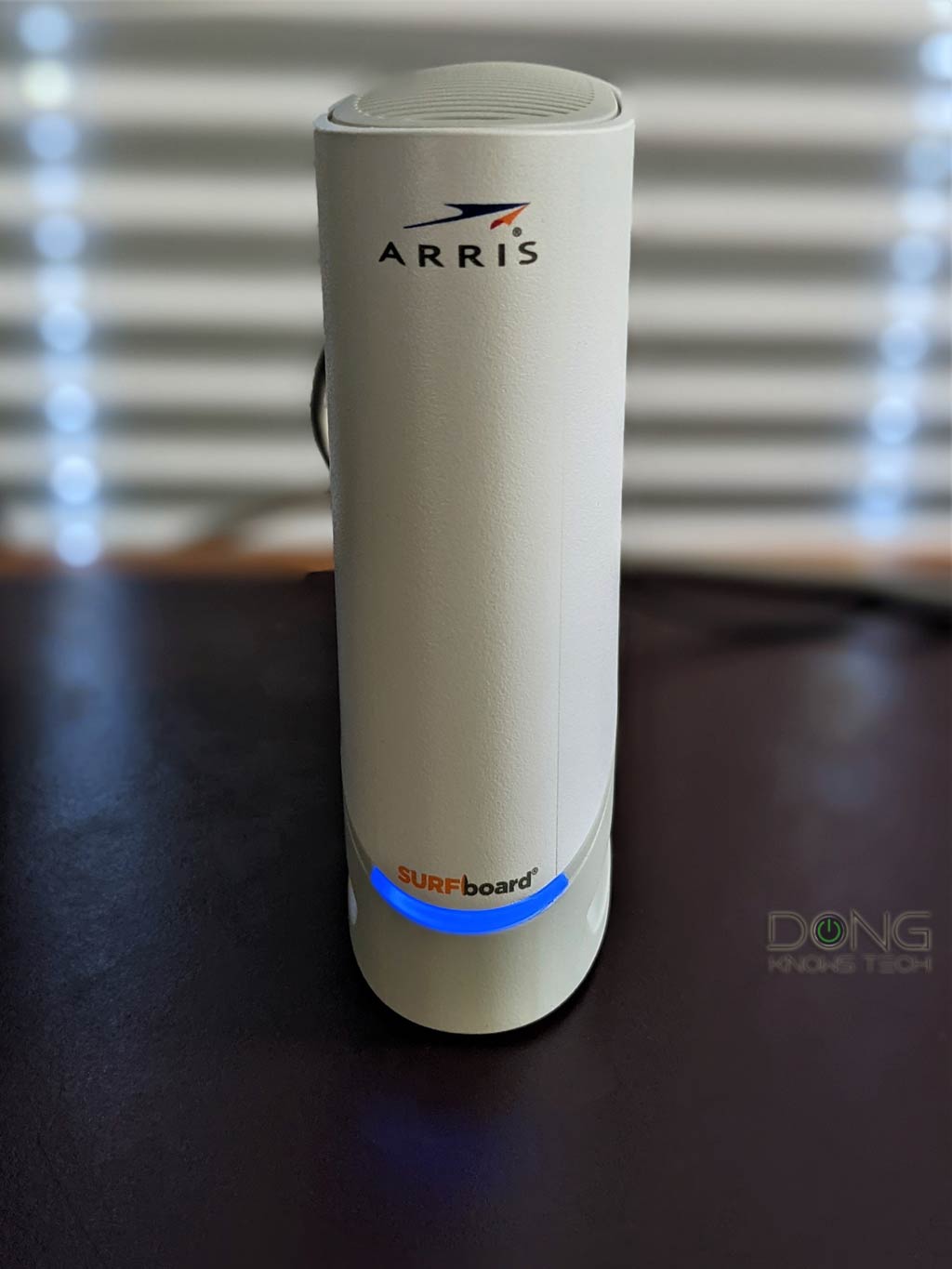


However, some modems, such as the ARRIS SURFboard S33, come with a single light that changes color to show the status. In this case, you must remember what color indicates it has no Internet connection.
Here’s what you can do at the modem if the broadband status light is off or shows that it has no signal from the provider:
- Check the broadband status light. It must show the correct color. In a traditional modem, the broadband light must be solid (green, blue, or white). If it’s not lid, red, or flashing erratically, ensure the service cable is intact and securely attached to the device. Then, you should:
- Give the modem a restart and wait a few minutes for it to boot up fully. Often, that fixes the problem.
- Reconnect the service line: Unplug it from the modem and reconnect it tightly.
If all that doesn’t fix the issue, then:
- Check to ensure there’s no outage in the area (or you can check that first before checking the modem.) If there’s no outage, then:
- Call your Internet provider. At this point, there’s nothing you can do. Tell the customer support agent you have no Internet signal at the modem. They’ll check on their end and fix the issues. Sometimes, if your modem no longer works or is supported, they will tell you to get a replacement.
If your modem appears fine, you might want to reconnect both ends of the network cable linking the modem and your router or even replace it to make sure.
A Fiber-optic ONT is more straightforward than a modem. It also has a broadband light often labeled as PON or has a star symbol.
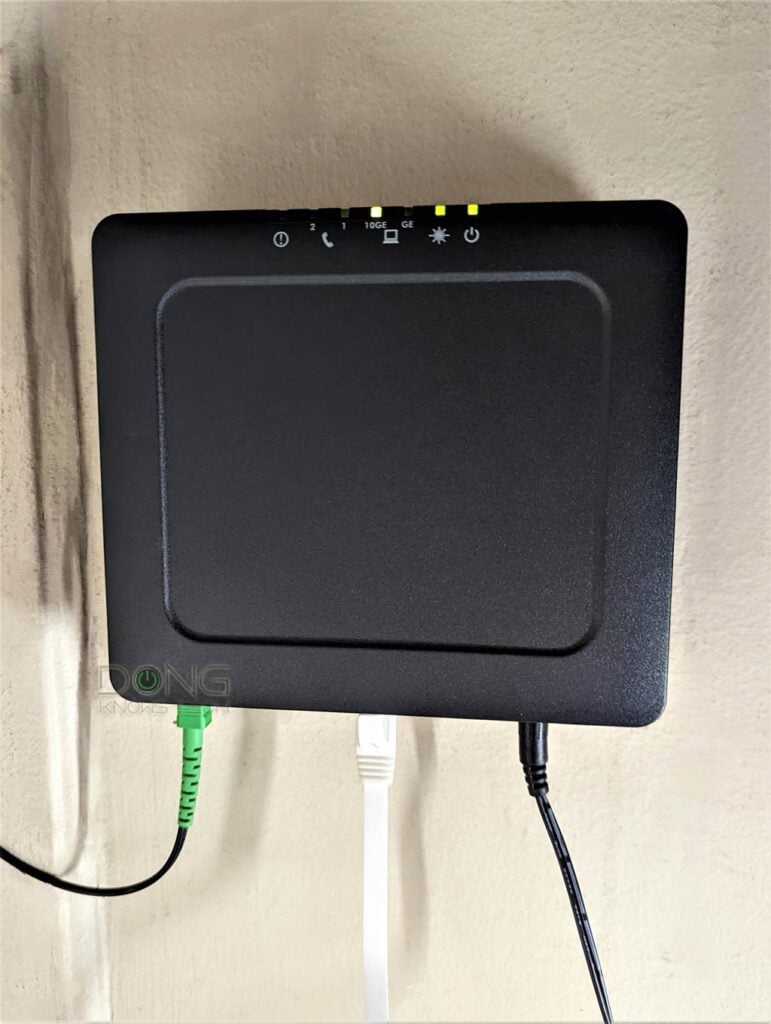

This particular ONT in the photo can also deliver a second Gigabit connection (not in use) and two phone lines (not in use).
This light has to be solid. After that, ensure the Ethernet shows the connection status between the ONT and the router’s WAN port is also in good shape.
There are three things you can do to troubleshoot an ONT—you can do one or all three, but be gentle with the wires involved:
- Restart the ONT itself—unplug it from power for about 10 seconds and plug it back in. Then, give it a few minutes to boot up fully.
- Reconnect the Fiber-optic service line—remove it from the ONT and then reconnect it.
- Reconnect the network cable connecting the ONT and your router. Sometimes, you might want to use a different cable.
In the photos above, the black cable is for power, and the green one is for the service line.
If that doesn’t fix the issue, you should call the provider to report it. There is nothing else you can do.
If your terminal device:
- shows a live Internet connection, and
- its connected wires are in good shape,
yet, you still have connection issues on your device, then it’s time to check your Wi-Fi router (or the router unit of your mesh system.)
2. Wi-Fi issues: What to do at the router
There are a couple of things you can do with the router. There are simple and advanced steps.
Simple things you can do with a router
Again, don’t forget the simple stuff:
- Give the router a restart—unplug it from power, wait for 10 seconds or so, then plug it back in. Now, give it a few minutes to boot up fully. That might fix the issue.
- Ensure the router’s Wi-Fi function is not turned off—many routers have an on/off switch for Wi-Fi. Generally, the router has a status light for each band (5GHz, 2.4GHz, or 6GHz). These lights need to be on.
Advanced steps in working with a router
These are general steps for advanced users or those comfortable with computers.
- Access the router’s web interface. Try updating its firmware to the latest.
- Access the router’s interface gain. This time, back up its settings, then reset it—yes, I do mean reset—and set up your network from scratch (or restore it from the backup file).
| Friendly URL (Internet connection required) | Default IP (a.k.a Default Gateway IP) | Username (no quotes) | Password (no quotes) | |
| Asus | http://www.asusrouter.com | 192.168.50.1 or 192.168.1.1 | “admin” | User-created during initial setup |
| AT&T Gateway | n/a | 192.168.1.254 | n/a | Access code printed on the hardware unit |
| Comcast (Xfinity) Gateway | n/a | 10.0.0.1 or 10.1.10.1 | “admin”, “cusadmin” | User-created during initial setup |
| D-Link | http://dlinkrouter.local | 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.200.1 | n/a | “admin” or printed on the hardware’s underside |
| MSI | http://msirouter.login | 192.168.10.1 | “admin” | varies (printed on hardware) |
| Netgear | http://routerlogin.com | 192.168.1.1 or 10.168.168.1 | admin | User-created during initial setup |
| Linksys | http://myrouter.local | 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 | n/a | “admin” (must be changed during the initial setup process) |
| TP-Link | http://tplinkwifi.net | 192.168.0.1 | “admin” | |
| Ubiquiti (UniFi console) | https://unifi.ui.com | 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.1 | User-created during initial setup | |
| Most Cable Modems | N/A | 192.168.100.1 | n/a | “admin”, “password”, “default” |
If you can’t access the interface or don’t know how to reset it via the interface, you can use the reset button. If all that doesn’t solve the problem, it’s time to get a new router or professional help.
Tips on how to get help with tech support
When you call for help, the person on the other end will try to troubleshoot the problem.
Often, figuring out the issue is the most time-consuming part of tech support. That’s because folks who need help tend to be emotional rather than technical and aren’t aware that, unlike their loved ones, gadgets don’t care about how they feel.
That said, when asking for help, it’s best to avoid giving the person who’s helping you non-technical information, such as your failed goal, frustration, sadness, needs, disappointment, or the fact that you didn’t do anything wrong—it’s OK, stuff happens.
Specifically, avoid saying stuff like: “I can’t get online,” “My internet/Wi-Fi/computer/phone/etc. is not working,” or “I have an issue connecting to Wi-Fi,” etc. None of that helps with troubleshooting because there’s zero information about what actually has happened.
Instead, be descriptive in explaining what has happened, such as when you do an ABC thing, you get an XYZ message. You can also give the person the error messages or information about what you see on the hardware, such as the status lights’ colors or behaviors.
It’s especially helpful to share photos of the error messages or the device itself. Visuals are always helpful in troubleshooting.
The takeaway
Like all things tech, a broadband connection is technical and dry. The best way to deal with it is to understand how things work and pay attention to the details. Getting frustrated or taking things personally won’t help.
Here’s the silver lining: If you pay attention and follow the instructions, it’s almost a guarantee that you can fix any connection issues. At worst, you just have to get new equipment or maybe a new service. Dealing with machines is always easier than dealing with our emotions. I speak from experience.
Dong’s note: I first published this post on January 18, 2019, and last updated it on February 13, 2025, to add more relevant information.



Thank your for all the great reviews, and the “how to articles” as I always find them interesting and helpful. Some I do not fully understand but still enjoy reading them. If you can, could you address the “blue question mark” the comes up on pictures in some websites.
I appreciate all you do for the tech consumer.
Regards,
George
Sure, George. If I catch your drift, that blue question mark often refers to an element, such as a picture, that’s not yet ready. Sometimes the element itself is missing, other times, the security settings might prevent it from loading or being downloaded.
Hi Don’t. Can you please help me? I have been given a really old PC but it’s in good condition. It was working but now I can’t get it started again. The lights on the modem are working except for one which is orange, the rest are yellow.
Many thanks
Jan
Looks like you were talking about two two different things, Jan. Also, the name is Dong.
Thank you as always for all the information you provide. Have been following you since you were at Cnet and still have your original videos of wiring a home network with the specific tools you use.
If a router company no longer is sending out updates for a specific router would that suggest it’s time for a new router?
Have been reading and re-reading your reviews of Wi-Fi 6E ones as mine no longer seems to receive these updates.
Firmware updates are not always good, George. They are necessary in case the hardware has vulnerabilities. If there’s no vulnerability and the vendor doesn’t want to add more features, then there’s no update. In short, you shouldn’t use updates as the only indicator of whether the hardware is good or bad or still supported. So this is case by case. Most of the time, no update is a good thing.
In many ways, firmware updates to routers are like recalls to cars.
Is it possible to have equipment issues with every device connected to a specific internet connection? As in, every phone, tablet, laptop, Chromebook, desktop that has ever been connected to this internet having issues with memory, losing files, showing no signal when there is signal or showing there is signal when there is no signal? Even printers do it. Brand new, old, Android or Iphone, Chrome OS and Windows and Linux. We have had issues wih my daughter’s internet for two years. From Nov. 2019 until she finally gave up in 2021, 30 techs had been to her home and all said there was nothing they could find and they reran wiring and all of that. Shes had her gateway swapped like 5 times as well. She is computer literate, never had issues before and we just have no idea what to do.
If there is no common machine OS that is experiencing the issues, but all of them, what should we do?
Technically, Beth, it is. It’s like if you put a filter on the water intake pipe of your home, all faucets within the house will be affected.
However, considering what you described, it’s likely your daughter’s devices (or her online accounts) have been infected with something. I’d recommend getting help from a local trusted professional.
I just signed up for optimum 2.5gb internet. They provide this device https://www.alticelabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/FL_GPON_FGW-Wi-Fi6_EN.pdf which I am now finding out is limited to what I can do with it. There is no GUI to login to configure it. So I cannot add my own AP on top since I cannot shut off the Wi-Fi it comes with. You can use a DOCSIS 3.1 Modem but they all have COAX input and the do not use COAX at all. So I am in a pickle and don’t know what to do. Any advice is helpful on my options. I do want to use my own devices.
You’re indeed in a pickle, Lewis. It would be best if you exchanged the gateway for an ONT, more in this post.
If that’s not possible, try turning the gateway into bridge mode, or you have to live with a Double NAT. More in this post.
Dong, love the site. Very useful information, guidance and reviews. I have a TP-Link A10 and for some reason the connection died one afternoon and lost IP connection completely. After diagnosing and isolating the issue, the IP issue was with the router as there was no IP listed in the status (blank). Called TP-Link SUpport and they suggested to do a MAC Clone with my computer. Im wondering why this worked and restored my TP LInk router and was able to get an internet addressed and connection ultimately? Can you explain that behavior?
I explained that in this post on MAC address, A.
Hi Do g
As always great info. I just had a situation where the tech cables the ONT to router using cat 3 cable (10baseT). So while I would get 300-800 meg it would not be sustainable.
Especially with zoom calls it would drop out all the time.
Thankful a young new tech called for help and the master tech fissured it out because the young tech was doing extra work that an experienced tech would have refused to do.
so very thankful for youth!
The only way I can figure out how to test for this is a 3-5 minute line saturation. Any thoughts on how to do this since a normal speed test is short?
Your message seemed broken, Daniel. But if I caught your drift, try downloading a large file. Like the Windows 11 ISO mentioned in this post and you’ll be able to see how the connection pans out over a few minutes.
I’m not sure how I found this blog, but maybe I can find the help and direction I need. I have xfinity internet (5ghz), and 3 computers (Imac desktop, and 2 macbook pro’s) that use the internet. Only 2 computers, at the most, are online at the same time. My Imac desktop (25 ft away in another room) connects wonderfully. My macbook pro also works great as to speed and connectivity where ever I go in the house. However, my wife’s macbook pro (the same model as mine) will only connect if she is within 2-3 feet of the router. Once she moves further away, it loses it’s connection and tells me I have to move closer to the router. This suggests to me that the issue must be with her computer, because my computers connect well and don’t drop their connections, even at further distances. I’ve tried to get help from a online service, and they can’t figure it out…..besides suggesting a full reinstall of the operating system (OS 10.12.6) My laptop has the same OS as my wife’s. Any suggestions on what direction to head to help my wife’s computer be able to move further away from the router and not have the connection dropped? Thanks for your time, effort, and quick reply in advance. Any help is appreciated.
It’s highly likely that’s your wife’s MBP’s Wi-Fi adapter has its antenna wires disconnected or loose, Wayne. You have to open the computer and check on it, it’s fairly easy and you’ll notice the adapters right away. It’ll look like one in this post (https://dongknows.com/steps-to-do-an-wi-fi-6-e-upgrade-on-a-computer/). Alternatively, you can get a USB adapter for that computer and stop using the current one.
One additional somewhat more advanced debugging technique esp. if you have your own cable modem separate from your router is that, by convention, almost all of the cable modem man’f make accessible an internal web server in the cable modem and have given it the same IP address, namely 192.168.100.1. So if you can get to your router successfully from a PC or laptop (i.e., your router is up and working), trying to open a web browser connection to 192.168.100.1 and then logging into the cable modem web server. Some cable modem web servers require a user id and/or password, and each vendor has their own default which you can usually search when your connection is up (so do this before you need to). Once logged in, there is usually a wealth of information available about the state of the modem, error logs, channel connection status, etc. One very useful feature on most of these is the ability to reboot your cable modem remotely, esp. useful if your cable modem is inconveniently located like on a different floor of your home from your PC. The default userid/password isn’t a terribly vulnerable security hole since the cable modem is on a non-routable private address so it can only be accessed from on your LAN, but if you want even mode security you can typically change it to something more private as well.
Good tip, Randall. Thanks.
Our entire community has a dedicated fiber ISP. My neighbors & I can connect to our ONT’s w/older AC-type routers [via ethernet cable to the router WAN], right “out of the box”, without any special setup or configuration. But we are unable to connect ANY newer AX-type routers. ASUS, Netgear & TP-Link service techs have been unable to assist us. Is there any difference in the AX router WAN [input] circuits?
Thanks!
That doesn’t make sense, Larry. If the connection works with an AC router, it will work with an AX router. What exactly did you mean by “unable to connect,” by the way? Because clearly, you *can* connect a network cable into the ports of the two parties. It’s physics.
I know it doesn’t make “sense”, but we can [repeatedly] connect new or old AC routers to our ONT’s and get to the internet, while we are unable to connect [get internet] w/three brand new AX routers. I thought there might be something different about the input/WAN circuits on the AX routers. The router techs – and our ISP techs are unable to assist us.
Currently, there are many AC routers on the market. But I assume this will not [soon?] be the case.
That’s super odd, Larry. You need to check the interface of the AX router to see what the error of the WAN connection is. Also, try these:
1. Restart the ONT and the AX router after the setup. In that order.
2. Copy the MAC address of the AC router that worked on the AX router that didn’t. Use the latter’s MAC clone.
And no, AC routers will still be on the market for years to come. AC is not going away anytime soon.
Thanks for trying to help us Dong. Unfortunately, power cycling and “MAC spoofing” do not help. It is a very interesting problem. All AC-type routers [and even desktop/laptop PC’s w/AC cards] will readily connect to the ISP ONT. Three brands of AX routers will not. [ASUS, TP-Link & Netgear]
To increase wifi coverage in my home I have connected a new Netgear [RAX50] router to a LAN port from an older AC router. But I would prefer not having to run [2] routers.
Very good article for the first steps but i was hoping there would be information about actually analyzing the status and event log. The specific (only) service provider here stock answer is that the problem is not there’s, even though multiple users report same problems. I don’t know what the boundaries are for Freq Pwr SNR or what some of the event log entries actually mean. Do you have that info posted or can point me to the correct place to find it? Thanks so much for sharing all this information
That’s specific to an Internet provider, Emma. Generally, when it comes to that, you need to contact the vendor or a professional.
So I tried putting the TP-Link M9plus into AP mode and hang it off my Linksys 1900AC+. I noted the same drops. So I hardwired to the Linksys
router and ran ping tests. Same thing happened. I believe the COmcast Cable modem is the problem and will have to get that swapped out.
I may put the Deco M9 back as the main router again instead of AP mode..
And a few days later, the drops have stopped.. I will probably remove the Linksys as the router and put the Deco M9 back at Router/Mesh to keep it
simple. Comcast must have fixed their issue.
Hello Dong! Great advice as usual. I’ve had intermittent issues with my internet. Switched modem and router and problem still remains. Had spectrum out to have a look and they confirmed everything was fine on their end. Very frustrating until I moved the modem away from the router and my Verizon cell booster. Is it possible these were interfering with the signal somehow? Much better since I moved it.
Definitely, David. Don’t use any “booster” devices (Wi-Fi or Cell). They are no good. Most cell phone now has the Wi-Fi calling feature anyway.
Hey Dong, has anyone developed a system / device or whatever, that can allow you to access the internet, when your primary internet goes down? Kind of like a “Backup” internet of sorts?
I thought about this the other day, when my internet went down and I could not view my wifi cameras.
That’s called Dual-WAN, David. Most routers can do that. You need two Internet sources.
Hey Dong, thanks for the reply…..Have you done a article on this, on this platform yet? It would be very educational… (hint hint)
Not yet on this feature specifically, David. But it’s relatively straight-forward. You need two Internet sources (Cable + DSL or cellular, for example), then you can set them up as load-balancing (if the two are of similar speeds) or failsafe.
Hi Dong,
Very impressed with your site and your advice!
Would you say in general that you get better/stronger results using your router’s dual-band smart connect rather than keeping the 2.4 and 5 G networks separate (I’m thinking about the Asus RT-AX3000 router)? Are there other settings you automatically change from the default settings that you would recommend for better performance?
Thanks,
Alan
Thanks, Alan. And no, the Smart Connect is just a matter of convenience. It has nothing to do with signal strength. The only benefit is it allows a device to automatically switch to the 2.4GHz band when the 5GHz one range, which is shorter, diminishes. So it might give you the elusion of signal strength and longer range at the expense of not being able to make sure your device will connect to the 5GHz band, which is faster at a close range.
Doug
A question on bouncing a router which I do weekly via a mechanical timer.
Upon reboot, my TCL tv which is an Ethernet connect direct to the router loses its Internet connection and I have to reset the network connection on the TCL Roku device to regain internet access. Any suggestions?
Thanks in advance.
I wouldn’t do that using a mechanical timer, Jerry. If the router has a restart on schedule feature, use it (that’s the only time when the term “bounce” is correct by the way). If not, just manually do it when you feel like or when it’s convenient, or when need be. I’d try restarting each of those devices manually, one at a time, to see if the disconnection happens. You’ll then find out where the problem is, the router or the TV. In any case, make sure you get their firmware to the latest.
I am so happy I found your blog and I absolutely love your information about the internet and wi-fi trouble shooting.I liked and it is wonderful to know about so many things that are useful for all of us! Thanks a lot for this amazing blog!!
This article provides us information regarding internet and wi-fi trouble shooting. I loved the way they have researched and presented it infront of us. Here you will get to know in detail about the topic which are in demand. I enjoyed alot while reading this article and would recommend other.
I have been having that problem intermittently for the last couple of months and Comcast has been unable to fix it. I was thinking maybe it was my computer. Thank you so much for writing this article. I printed it out and will try to follow it.
Thank you for your help-you have helped me before and I really appreciate it!
Best, Marsha
You’re welcome, Marsha! 🙂